What is biometric authentication?
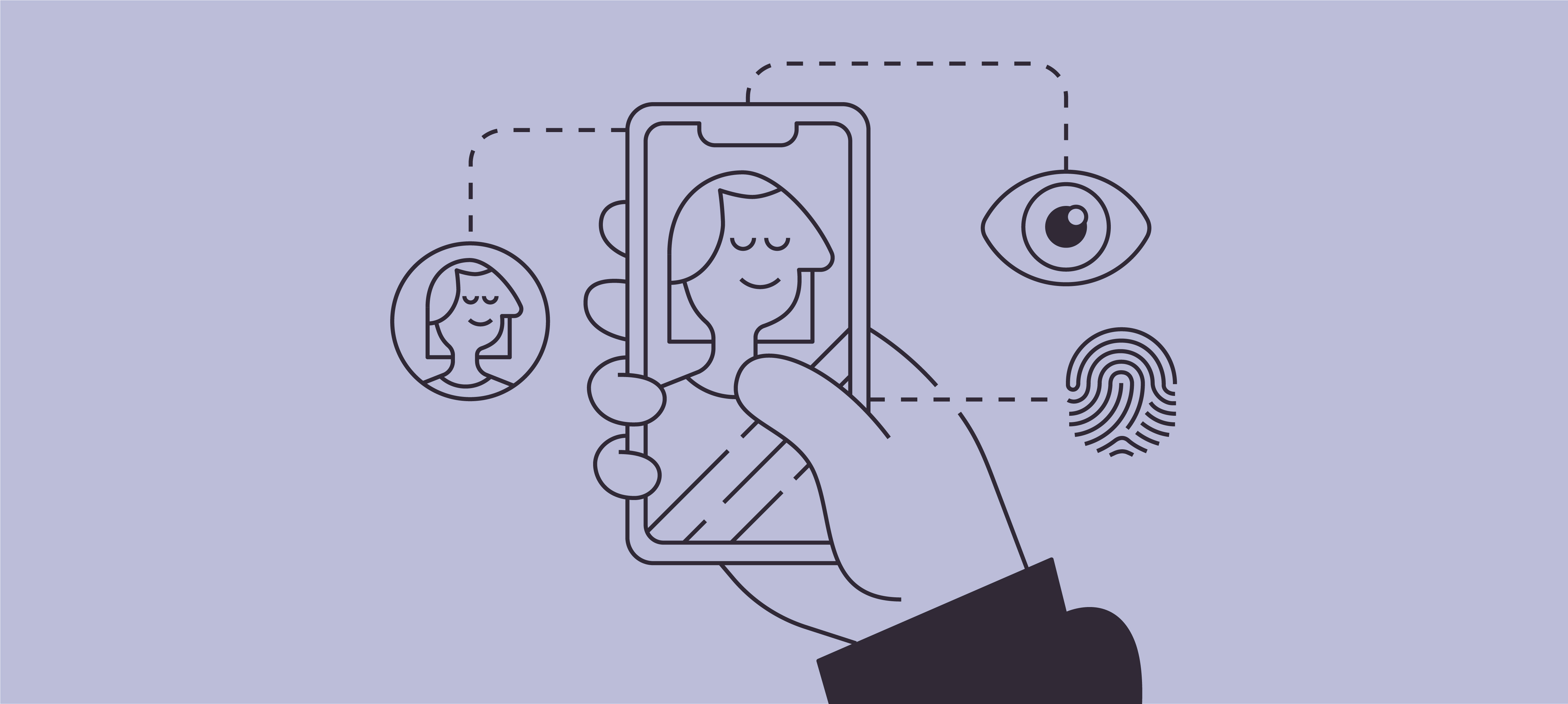
Biometric authentication is a security measure that requires people to verify their identity by providing a unique biometric feature. The word “biometrics” refers to an individual's unique biological characteristics. Within the authentication process, it usually requires a feature like a fingerprint, facial, or eye recognition.
The use of biometrics is growing and the market for biometrics is expected to triple by 2027 compared to 2019. Because it combines a high level of security with a frictionless experience, biometric authentication is often seen in regular authentication processes as well as two-factor and multi-factor authentication.
Types of biometric authentication methods
There are three primary types of biometrics used for authentication purposes. Within the authentication process, it refers to the Something you are factor.
1. Facial recognition
Of all the available biometric features, facial recognition is perhaps the most efficient. It requires little effort as you merely have to look into a camera to authenticate yourself. Thanks to this ease of use, facial recognition has become a natural part of our daily lives, and people regularly use it to unlock smartphones. The facial recognition process relies on a face scan which either succeeds or fails to match it with the one stored in the system.
2. Fingerprint recognition
Fingerprint recognition has been around even longer and is still widely used in certain situations and industries. A user scans their fingerprint, which the system registers, granting access if it matches the fingerprint data stored in the system. The process is not quite as smooth as facial recognition. It can also be negatively impacted by the finger being dirty or wet, as well as the state of the fingerprint scanning surface itself.
3. Eye recognition
There are two ways to identify a person through eye recognition: retinal scan or iris scan. Since both the iris and retina are unique for each individual, eye recognition is considered to be the most secure method of biometric authentication.
For retinal scans, the blood vessels in the eye are illuminated by a light and compared with the data stored in the system. Iris scans work in a similar way: They take a picture of an eye in order to detect a unique pattern of its iris, which can authenticate the individual.
4. Voice recognition
In voice recognition, an individual provides a voice sample, which is processed to create a "Voiceprint." This Voiceprint captures unique vocal characteristics such as tone, pitch, and speech patterns. When the person later seeks to verify their identity, they provide a new voice sample. The system analyzes this sample and compares it to the stored Voiceprint. Based on the similarity between the two, the system confirms or denies the identity.
Is biometric authentication secure?
Biometric authentication is considered to be a highly secure method of verifying identities, because biometric features are unique to each individual. Not only are they harder to steal or fake but–unlike passwords–biometrics are not something a user can forget. They authenticate themselves by simply being who they are.
The introduction of biometric authentication has been crucial in increasing security compared to passwords, which have been responsible for around 80% of security breaches. This is because passwords are easily stolen if people write them down, share them with others, or reuse them for other online accounts.
Since biometric features are known to be harder to steal, hackers are less likely to attack systems that rely on biometrics, focusing instead on easier targets, like passwords. This is also true for authentication processes that use two-factor authentication (2FA) or multi-factor authentication (MFA), as breaching two separate authentication steps requires far more advanced techniques.
Therefore, combining 2FA or MFA with biometric authentication can significantly increase security for users and businesses.
What are the business benefits of biometric authentication?
There are three main benefits for companies that incorporate biometric authentication in their processes:
- Increased security
- Better customer onboarding
- Improved customer satisfaction
Learn more in our article about the customer benefits of biometric authentication
Most companies will consider at least some of the above to be critical to their online success as a business. Some industries care more about security while others may prioritize usability. In either case, biometrics offer an efficient way to accomplish both of these goals and boost satisfaction through improved user experience and safety.
What are the challenges of biometrics?
Despite its benefits, there are a number challenges in biometric authentication.
Challenges in biometric accuracy
Various factors can influence the accuracy of biometric authentication. For facial recognition, issues such as facial expressions, lighting, or the angle of the face can lead to denied access, resulting in frustrated users. Similarly, external conditions like wet weather, sweat, or dirt can interfere with fingerprint scanning.
Concerns about biometric data security
The sensitivity of biometric data raises significant concerns about misuse or unauthorized access. Unlike passwords, biometric identifiers cannot be reset if compromised. This makes them a potential target for cyberattacks, which can heighten user anxiety about the security of their data.
Biases in facial recognition systems
Studies have revealed that some facial recognition systems are biased, particularly against women, elderly individuals, children, and people of color. These biases can result in exclusion, poor user experiences, and diminished trust in the system. For users, such issues emphasize broader concerns about fairness and reliability in biometric technologies.
Biometric authentication in electronic identities
In many European countries, national electronic identities (eIDs) are used as a method of authentication. Users have unique access to their own eID, which is used to verify their identity online. Electronic identities are often used for public services and are also widely adopted by private companies that require a high level of security.
Some eIDs also provide biometric authentication, which simplifies the verification process. Using biometrics gives companies the opportunity to leverage eIDs to create a smoother login process for their users.
Currently, the following eIDs allow the use of biometric authentication:
Danish MitID
MitID is the national eID used by Danish citizens to log in to all government services, financial institutions, as well as many private businesses. With MitID, you are able to use fingerprint or facial recognition to authenticate your identity.
Norwegian BankID with biometrics
Norwegian BankID has recently introduced biometric authentication through their new version of the identity scheme: the BankID app with biometrics. The old mobile BankID used a technology based on SIM cards and temporary passwords. By switching to app-enabled biometrics, BankID has managed to create a significantly more secure and user-friendly eID.
Read more about the differences and how biometrics significantly improves the use of BankID.
Swedish BankID
Swedish BankID is one of the oldest and most widely used eIDs in the world. The company first started providing eID authentication in 2003 and allows biometric authentication through fingerprint and facial recognition.
Want to learn more about biometric authentication with eIDs?
Criipto is an official provider of European eIDs like Danish MitID, Norwegian BankID with biometrics, Swedish BankID, and Finnish Trust Network (FTN).
We ensure that businesses and developers can easily implement eIDs with biometric authentication in their website or application through a simple integration process. Read more about electronic identities or get in touch with us if you are interested to learn more.


